Touch technology is changing how people use computers and other digital devices. This includes everything from cell phones to advanced VR training systems (Source). With organizations trying to build interfaces that feel more real, knowing the difference between haptic vs tactile technology is critical. It helps teams pick the best technology for what they're building, whether it's for their product or a training program.
Introduction
Haptic feedback has grown immensely. VR can now mimic forces and movements realistically. People sometimes confuse haptic feedback with tactile feedback. To tell them apart, it helps to understand their similarities and differences. Knowing what kind of touch experience you need helps when choosing the proper technology.
In this blog, we define both concepts, compare their core differences, and provide clarity on where each excels in real-world applications, with a special focus on haptic vs tactile.
What Is Tactile Feedback?
Tactile feedback refers to the sensations on your skin, this includes being able to feel vibrations, pressure, or texture. This technology provides users with simple signals without needing any visual or auditory signals. Some common examples of this are phone vibrations, braille displays, and the textures on control panels.
Tactile tech uses vibration motors called actuators inside devices. On activation, these generate physical sensations, which communicates to users that they did something, such as pressing a key or acknowledging a message. This makes it light and cost-effective, so it works well for devices that need simple touch signals that people can rely on.
Tactile feedback is commonly used in consumer electronics and industrial training tools when signals need to be quick, cost-effective, and relevant.
By offering reliable and straightforward cues, tactile feedback ensures essential communication without requiring complex hardware or high processing power.
Haptic feedback goes beyond the sense of touch; it integrates force, motion, and kinaesthetic feedback. Haptic feedback imitates touch as we experience it in the real world, allowing us to sense weight, resistance, texture, or motion in virtual settings. Owing to this, haptic tech goes beyond basic notifications to produce realistic interactions (Source).
This is quite useful in VR training, when people need to imitate detailed manual tasks. This realism helps them learn faster, build stronger muscle memory, and boosts their confidence. As more industries use spatial computing, haptics will keep bridging the divide between digital learning and doing things physically. There are three types of haptic feedback:
Vibrotactile feedback uses vibrations to show interactions or events. You can find it in gaming controllers and smartphones.
Force feedback creates a sense of resistance. It is used in simulators and for robotic control.
Thermal and kinaesthetic feedback uses temperature changes or body movement. It can enable very realistic simulations for training in medicine and industry.
Haptic feedback is quite adaptable, making it quite useful in creating digital experiences that are real, especially where realistic experiences are required for training or decision-making.
Key Differences Between Haptic and Tactile
When it comes to haptic vs tactile, the main difference lies in their scope and depth of immersion. Tactile feedback deals with surface cues. Haptic feedback includes force, motion, and kinaesthetic sensations to feel real. Knowing these differences is important when picking the correct method for product design or company training (Source).
Here’s a quick comparison of both based on key features:
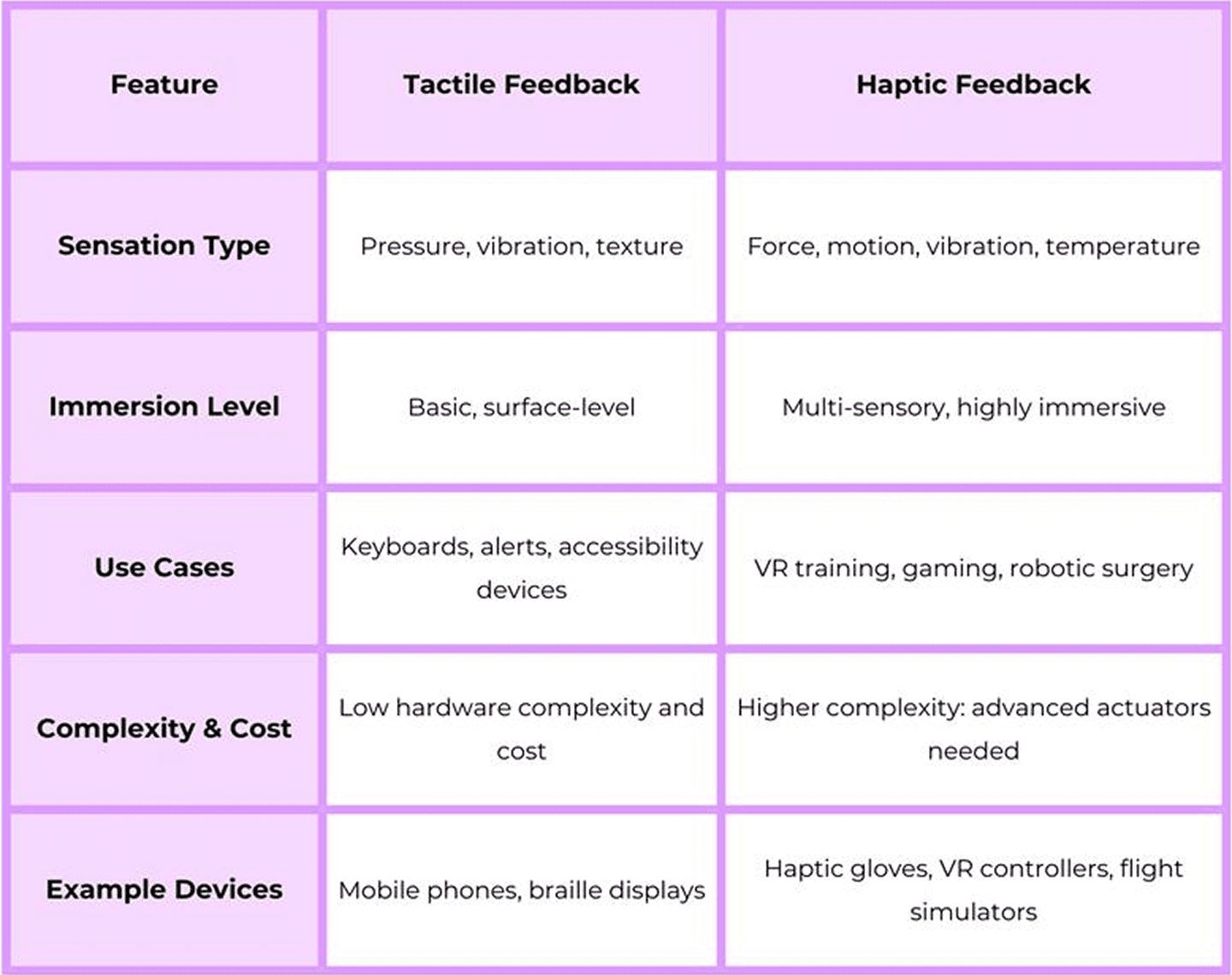
A comparison of the two shows that industries tend to use tactile feedback to convey simple signals, while haptic feedback is used in high-resolution simulations where spatial awareness is required.
Applications of Tactile Technology
Tactile technology is commonly used owing to the simple user feedback in devices we interact with daily. Cell phone alerts, Mobile notifications, ATM keypads, and wearable fitness trackers make use of tactile signs for quick, cost-effective interactions. Aside from consumer tech, tactile feedback is critical for accessibility tools like braille displays and machinery control systems for visually impaired users.
Tactile technology's simplicity and low energy requirements make it suitable for industries where experiences are not complex and reliable alerts are needed at a low cost. Its strength lies in low cost and reliability, making it an important part of the haptic vs tactile discussion. Tactile feedback continues to be a scalable and useful option in various industries for simple confirmation signals and to improve accessibility.
Applications of Haptic Technology
Haptic technology improves immersive interactions, especially in VR and AR. In VR training, haptic gloves with feedback let users sense resistance or vibrations while using virtual machines (Source). This realism increases muscle memory and improves safety in simulations for manufacturing, aviation, and healthcare. Haptics improve automotive safety by alerting drivers through steering wheel vibrations. They also aid surgical robots from a distance by giving them a sense of touch.
Haptic technology merges digital and physical sensations, to create an engaging experience which is beyond basic touch. This is extremely useful for training. When we compare haptic vs tactile applications, haptics clearly leads in creating lifelike, immersive environments, while tactile dominates in simple, everyday alerts.
Why Is There Confusion Between the Two?
Haptic feedback is a subset of tactile perception, both of which fall under the umbrella of touch. While both involve a sense of feeling, haptic feedback mechanisms are more intricate. The misuse of the term haptic feedback, to refer to simple vibrations, creates this confusion. By understanding haptic vs tactile, businesses can avoid mislabeling and ensure they are selecting the right technology for their needs.
When designing experiences, product teams can prevent issues by clearly defining touch technologies. This avoids both over-specification and under-use.
Which One Should You Use?
When deciding between haptic vs tactile feedback, consider your goal. Tactile feedback often works for simple alerts and budget-friendly setups. Haptic feedback is often better for more advanced uses. Some examples are virtual reality training, robot control, or medical simulations. Things to keep in mind are your budget, the hardware and how users will interact with it.
Businesses can improve how users experience their products and how well they learn by choosing tech that fits their needs.
Future Trends in Haptic and Tactile Technology
Tactile and haptic technologies are changing quickly these days. Tactile actuators now are thinner and use less power. Haptic systems use AI to change their responses. They also have multi-sensory feedback. These changes will help the next AR/ VR apps, robots, and even car interfaces. This will make touch interfaces more lifelike.
The future involves merging touch-based and haptic tech to make interactions feel natural across different fields.
Conclusion
The discussion on haptic vs tactile feedback isn't about superiority but suitability for a specific task. Tactile tech is great for its simplicity and ease of use, but haptic tech is better at making training and simulations feel real. For businesses creating advanced interfaces, knowing the differences leads to better spending and better user experiences.

